Here, we will explain the placement flow by going through the functionality of the major modules in the placer. Of course, you can also make full use of the Doxygen diagram to trace the call graphs to understand their relationship. We try to avoid multi-level class during implementation so it is easier for beginners to trace the call graphs.
Data Containers:
We use a set of containers to store and analyze the information/data of design, device and placement.
- DesignInfo: Information related to FPGA designs, including design cells and their interconnections.
- DeviceInfo: Information class related to FPGA device, including the details of BEL/Site/Tile/ClockRegion.
- PlacementInfo: Information related to FPGA placement (wirelength optimization, cell spreading, legalization, packing)
- PlacementTimingInfo: The container which record the timing information related to placement.
Placement Prossors:
We implement a set of placment processors, which will modify the data/information in the containers to improve the placement quality according to given metrics.
- GlobalPlacer: accounts for the general iterations in global placement including wirelength optimization, cell spreading, legalization, area adjustion...
- a. ClusterPlacer: cluster nodes in the given netlist and place the clusters on the device based on simulated-annealing as initial placement.
- b. WirelengthOptimizer: builds numerical models based on the element locations and calls solvers to find an optimal solution of the placement.
- c. GeneralSpreader: accounts for the cell spreading, which controls the cell density of specific resource type, under the device constraints for specific regions.
- d. MacroLegalizer: maps DSP/BRAM/CARRY macros to legal location
- e. CLBLegalizer: maps CLBs (each of which consists of one site) to legal location. e.g. LUTRAM, except those CLBs in CARRY8_Chain.
- InitialPacker: identifies macros from the design netlist based on pattern matching
- IncrementalBELPacker: incrementally packs some LUTs/FFs during global placement based on their distance, interconnection density and compatibility
- PlacementTimingOptimizer: based on the timing information and the placement information, adjusts some terms in the quadratic models which can improve the timing.
- ParallelCLBPacker: finally packs LUT/FF/MUX/CARRY elements into legal CLB sites in a parallel approach.
Novel Solutions:
Compared to previous work, we proposed a series of novel solutions for FPGA mixed-size placements and meanwhile we provide a set of optimized extension of some latest works from the perspectives of cell spreading, congestion mitigation, clock legalization, packing and timing optimization. Here we prepare some explanation for users who are interested in the details, (where the devil is. LOL).
- Wirelength Optimzation in Quadratic Placement Flow : the simulated-annealing-based initial placement and some important factors/terms in the quadratic placement target function.
- Parallel Cell Spreading : the parallel solution to cell spreading for large designs with many macros and the sensitivity of partitioning-based algorithm.
- Parallel Progressive Macro Legalization : high-quality high-performance progressive macro legalization of mixed-size elements in FPGA.
- Mixed-size Packing : high-performance parallel packing considering macros and clock legalization
- Optimization for Timing, Clocking and Congestion : some included optimization for timing, clocking and congestion
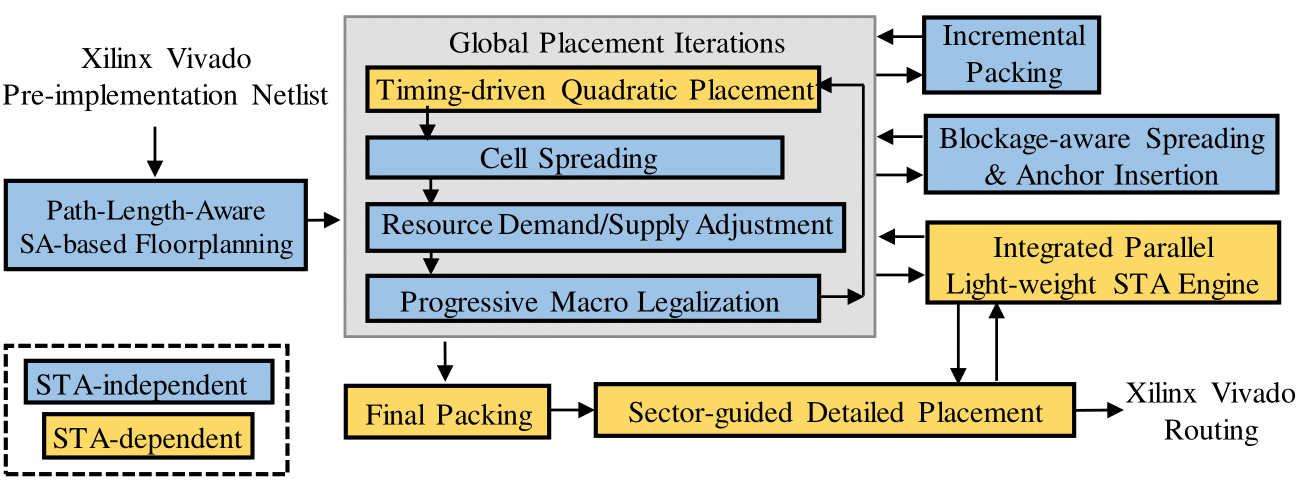
The AMF-Placer Workflow
Below is the overall flow of AMFPlacer and a visualized procedure is shown in the figure below. If you are interested in the details of AMFPlacer runtime behaviors, you can find the concrete explanation here: (Runtime Log Explanation).
- AMFPlacer will be constructed based on the DesignInfo and DeviceInfo.
- At the beginning, AMFPlacer will construct the PlacementInfo based on the DesignInfo and DeviceInfn.
- The element attributes, locations and densities will be initialized in the PlacementInfo.
- InitialPacker will be called by AMFPlacer to identify PlacementMacro and PlacementUnpackedCell from the design netlist.
- The PlacementTimingInfo inside PlacementInfo will be initialized by constructing a TimingGraph and checking the level of DesignCell in their corresponding timing paths.
- GlobalPlacer will cluster the netlist based on clock information and the connectivity and initially place the cluster on the device based on SAPlacer.
- GlobalPlacer will go through some global placement iteration (wirelength optimization, cell spreading, legalization)
- PlacementInfo will set a more fine-grained cell density grid.
- (Again) GlobalPlacer will go through some global placement iteration (wirelength optimization, cell spreading, legalization).
- IncrementalBELPacker will pair some LUTs and FFs based on their locations as an intermediate process for later packing.
- PlacementTimingOptimizer will enhence some net weights for timing optimization.
- GlobalPlacer will enable PlacementInfo (i.e., set neighbor displacement upperbound to a positive value) to conduct packing-aware (Improved UTPlacerF solution, considering cell resource, timing and net density. Enable earlier cell packing determination based on history analysis. Enable parallel exception handling.) Please note that congestion-aware cell area adjustion will be automatically enabled during global placement according to the placement convergence progress.
- Finally, when global placement converges, ParallelCLBPacker will pack the elements into the corresponding DeviceSite / DeviceBEL.