Optimization for Timing, Clocking and Congestion
Simply optimizing wirelength will not make a placement feasible on FPGA device for practical applications so AMF-Placer has taken timing, clocking and congestion into consideration. For these perspectives, AMF-Placer includes the following optimization techniques:
We adapt this high-performance algorithm to our mixed-size placement scenarios with several major modifications:
1.The current version of AMF-Placer includes a graph-based timing analysis module which can identify elements in the long datapath. The timing model is based on simple polynomial regression. Based on this kind of information, the nets between elements will be enhanced accordingly to improve the timing result. A comprehensive static timing analysis will be available in a few months. Below is an example comparing the timing analysis results of AMF-Placer and Vivado: the left one is the critical path identified by AMF-Placer in OpenPiton and the right one is the critical path identified by Vivado in OpenPiton.
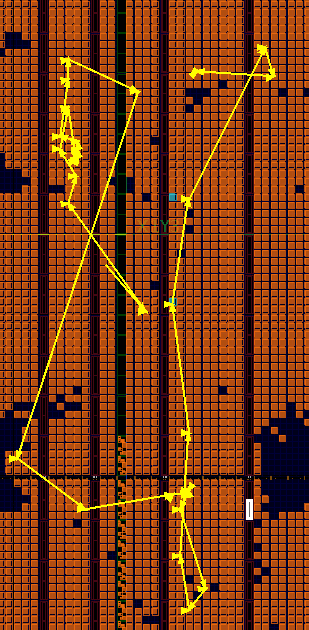
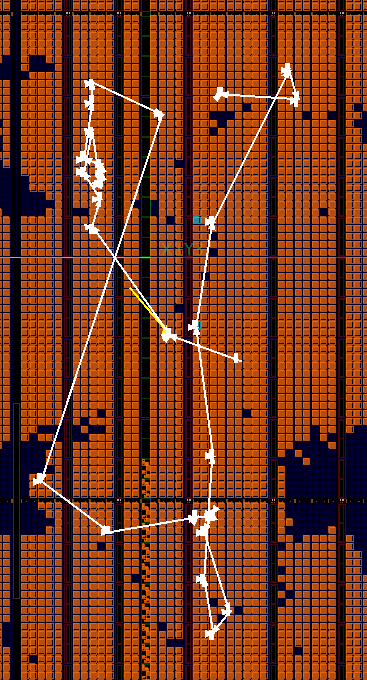
2.To lower the legalization overhead and the disturbance to the final convergence, we introduce quadratic pseudo nets to pull elements into their major clock regions (or fence regions). For each global placement iteration, the anchors of the pseudo nets and the "strength" of the pseudo nets are updated according to the relative location of the elements and the target regions. Meanwhile, for the half-column legalization of clocking (e.g.m >12 clocks in a half-column), AMF-Placer will inflaten elements in the clocking congestion region to lower the clocking legalization difficulty.
3.To consider the global congestion and local congestion, AMF-Placer solves the problem by controlling the area supply and demand. After congestion estimation, the local congestion can be more effectively resolved by reducing the area supply in the congested bins while the global congestion can be more effectively resolved by increasing the area demands of the elements. The placement congestion level of AMF-Placer is similar to Vivado and below is a figure for the most congested benchmarks (MiniMap2 with PCIE banks and OpenPiton with DDR Interface):
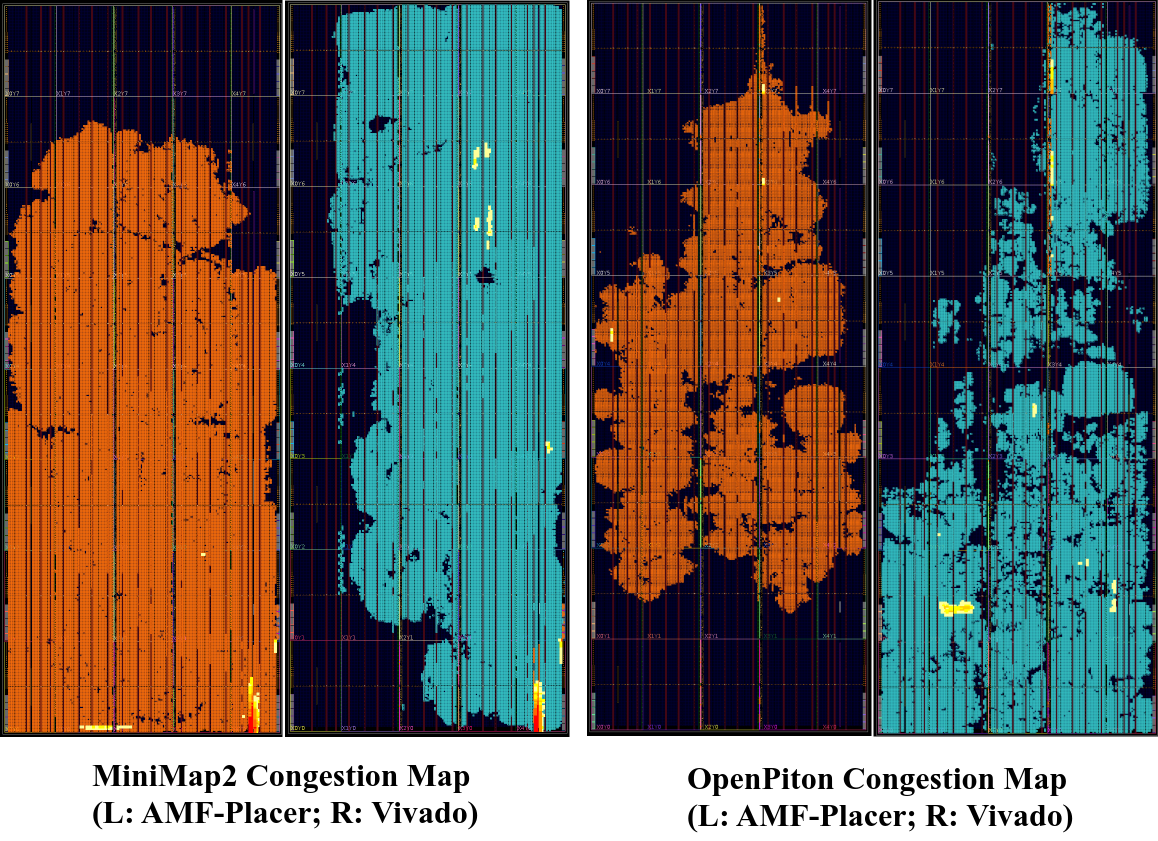
For source code details, please check the classes: PlacementInfo and PlacementTimingInfo.
References:
[1] J. Chen et al., "Clock-Aware Placement for Large-Scale Heterogeneous FPGAs," in IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, vol. 39, no. 12, pp. 5042-5055, Dec. 2020, doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2020.2968892.
[2] Chak-Wa Pui et al., "RippleFPGA: A routability-driven placement for large-scale heterogeneous FPGAs," 2016 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), 2016, pp. 1-8, doi: 10.1145/2966986.2980084.
